Green Earth Carbon Solutions has millions of high-quality carbon offsets/credits available!
Our Team
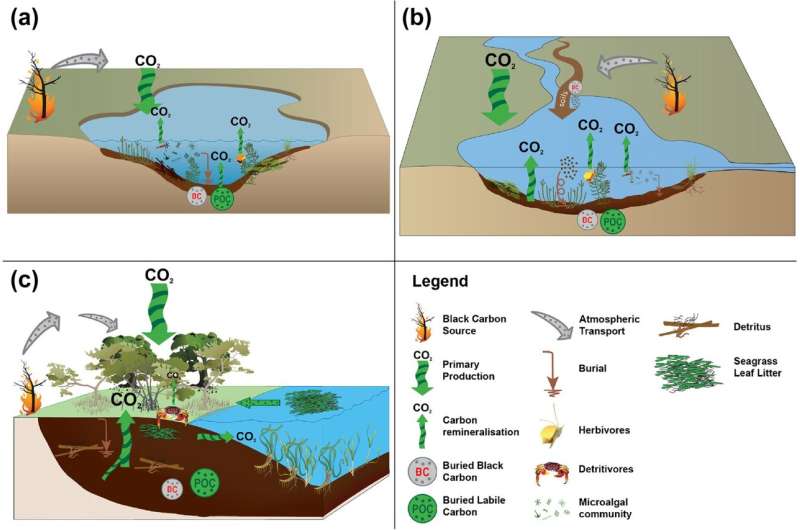
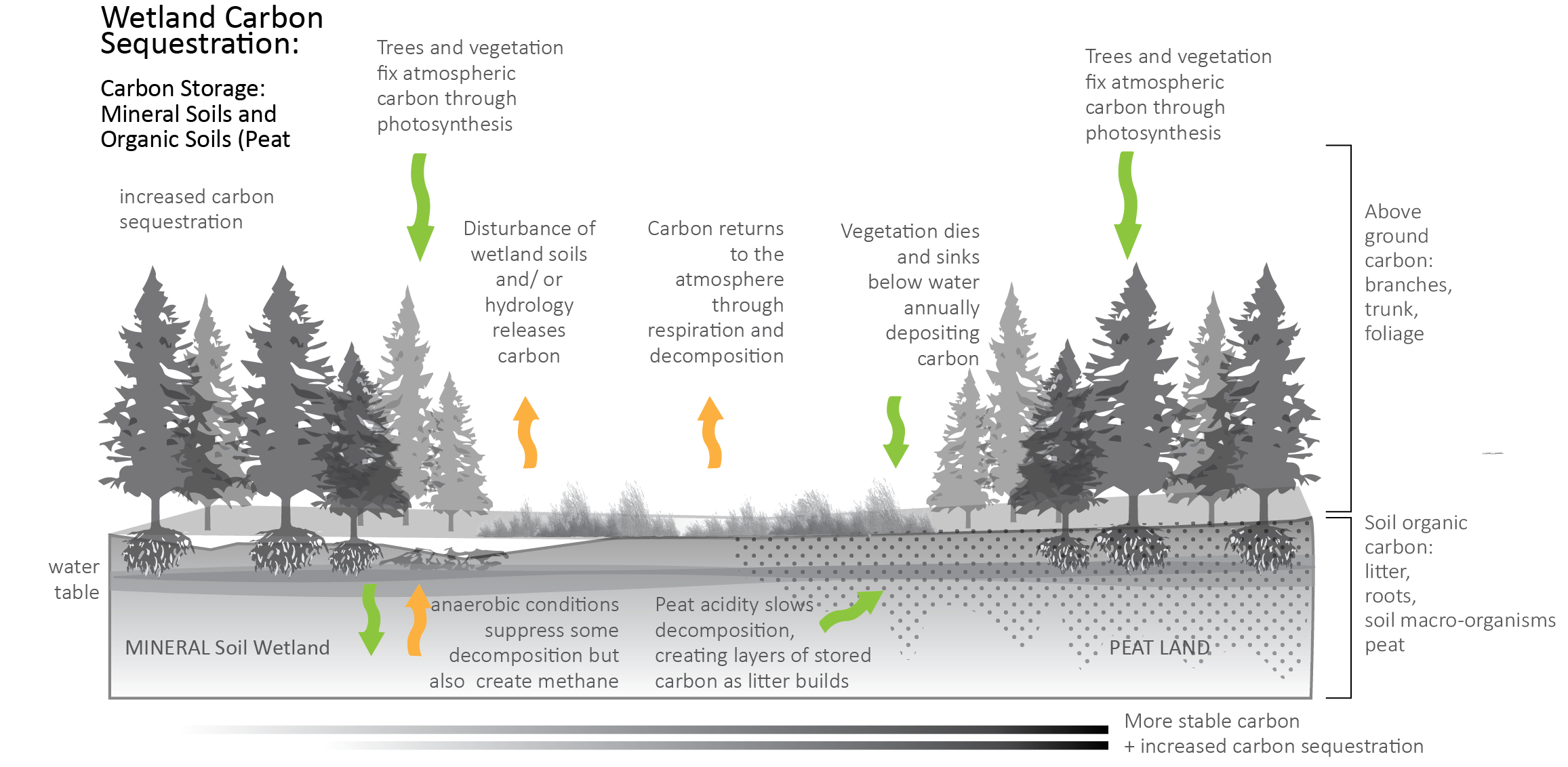
Wetland restoration is an effective strategy to sequester and store atmospheric carbon dioxide, mitigate climate change, and promote biodiversity conservation. Here's how it works:
Why wetlands?
- Carbon storage: Wetlands can store significant amounts of organic carbon in their soils, vegetation, and aquatic ecosystems.
- High carbon density: The unique combination of waterlogged conditions, plant growth, and microbial activity creates a high-carbon-density environment that can sequester large quantities of CO2.
- Long-term storage: Carbon stored in wetlands can remain there for centuries or even millennia.
Wetland restoration techniques
- Revegetation: Planting native vegetation species to re-establish the natural hydrological and ecological processes within a degraded or restored wetland area.
- Hydrologic restoration: Restoring water flow, depth, and duration to mimic pre-disturbance conditions, promoting healthy plant growth and carbon sequestration.
- Soil amendments: Adding organic matter (e.g., compost) to improve soil fertility and structure, enhancing microbial activity and carbon storage potential.
- Invasive species removal: Eradicating non-native plants that can outcompete native vegetation for resources, promoting biodiversity conservation.
Benefits of wetland restoration
- Carbon sequestration: Wetlands can store significant amounts of CO2 from the atmosphere, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
- Biodiversity enhancement: Restored wetlands support a wide range of plant and animal species, improving ecosystem resilience and function.
- Water quality improvement: Healthy wetland ecosystems help maintain water quality by filtering pollutants and sediments out of surface waters.
- Flood control: Wetlands can act as natural buffers against flooding events, reducing the risk to nearby communities.
Challenges and considerations
- Land availability: Finding suitable land for restoration efforts may be limited in areas with high population density or competing land uses (e.g., agriculture).
- Costs: Restoring wetland ecosystems requires significant investment in planning, design, implementation, and maintenance.
- Community engagement: Effective communication and collaboration are essential to ensure that local communities support and participate in restoration efforts.
Examples of successful wetland restorations
- The Everglades Restoration Project (USA): A comprehensive effort to restore the vast freshwater ecosystem in south Florida, focusing on hydrologic restoration and vegetation re-establishment.
- Wetlands for Water Initiative (Canada): An initiative aimed at restoring degraded wetlands across Canada's provinces, prioritizing water quality improvement and biodiversity conservation.
In conclusion, wetland restoration offers a promising strategy to sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere while promoting ecosystem services like flood control, water filtration, and biodiversity enhancement.
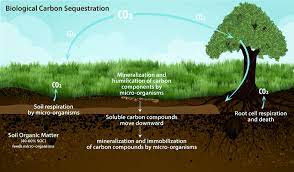
Biological Sequestration refers to the process of capturing atmospheric CO2 through biological means, such as photosynthesis in plants or microbial activity in soils.
Types of Biological Sequestration:
- Photosynthetic Carbon Sequestration: Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere during photosynthesis and store it within their biomass.
- Soil Microbial Carbon Sequestration: Soil microorganisms break down organic matter into stable carbon compounds that can remain in soils for centuries.
Mechanisms of Biological Sequestration:
- Photosynthetic Pathway: Plants absorb CO2 through stomata, and the energy from sunlight is used to convert it into glucose.
- Carbon Fixation: The enzyme RuBisCO (Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase) fixes atmospheric CO2 onto a five-carbon sugar molecule called ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate.
- Soil Microbial Carbon Cycling: Soil microorganisms break down organic matter into simpler compounds that can be stored in soils for extended periods.
Benefits of Biological Sequestration:
- Climate Change Mitigation: By capturing atmospheric CO2 through biological means, these processes help mitigate climate change.
- Ecosystem Services Preservation: These mechanisms contribute to maintaining essential ecosystem functions such as pollination, pest control, and nutrient cycling.
- Soil Health Improvement: Biological sequestration can enhance soil erosion, water use, or resource extraction), making it challenging to implement regenerative practices.
Mechanisms:
1. Photosynthesis in plants absorb CO2 from atmosphere during photosynthetic carbon sequestration these processes are critical challenges, Regenerative agriculture offer a unique opportunity for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting ecosystem services of soils. By adopting such methods farmers can help mitigate climate change while improving soil health.
Key principles:
- Soil Carbon Sequestration: This process involves using regenerative agricultural practices to capture atmospheric CO2 through photosynthesis, converting it into organic matter, and microorganisms.
- Soil Conservation:** Regenerative agriculture focuses on preserving the structure of soils such as cover cropping, crop rotation, mulching, and integrating crops that promote soil biota.
- Crop diversity: Planting a variety of crops like legumes or incorporating perennials can improve carbon sequestration through photosynthesis in plants with nitrogen-fixing crops to reduce synthetic fertilizers.
- Soil amendments:** Incorporating organic matter into soils from animal waste materials helps increase the capacity for soil microorganisms that break down these compounds.
Carbon Sequestration Mechanisms:
- Crop rotation periods: Plant biomass and enhance carbon sequestrations, and improve microbial activity in crops such as winter cover cropping mechanisms:**
1. Photosynthesis in plants absorb CO2 from atmosphere:** Plants capture atmospheric through photosynthetic processes into glucose which is stored within their tissues for extended periods. 2. Soil Microbial Carbon Sequestration**: Plant biomass during growth can be converted to carbon-rich compounds that are eventually broken down by microorganisms and sequestered carbon.
Regenerative agriculture practices:
- Carbon Cycling: Regenerative agriculture promotes soil biota diversity, which helps stabilize organic matter into stable carbon forms. 2. Crop rotations with legumes improve nitrogen fixation**: Planting crops like legumes can reduce synthetic fertilizers use**: By reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers in soils regenerative agriculture practices contribute to mitigate climate change.
- Improved water retention: Regenerative agriculture enhance soil's capacity, and retain moisture levels of water pollution through runoff and nutrient loss.
Water efficiency:
1. Soil conservation methods improve crop yields due to improved soil fertility. 2. Crop rotations**: Rotating crops with legumes nitrogen-fixing:
1. Legume-based cropping systems**: SHI) Regenerative Agriculture Program focuses on improving soil health, biodiversity, water retention capacity while reducing synthetic fertilizers use 3. The Savory Institute's regenerative agriculture research program that compares various farming practices and their impact on carbon sequestration. 4. Carbon sequestration.
Key considerations:
1. Regenerative Agriculture: This approach focuses on improving soil health through holistic land management strategies to promote ecosystem services while mitigating climate change:** Despite the benefits of Regenerative agriculture, requires large-scale adoption changes in farming practices and policies that may face resistance from existing agricultural systems.
2. Soil carbon sequestration: Accurately measuring carbon can be challenging due to various factors like soil type or management variations.
Key principles for successful implementation:
1. Soil conservation**: Regenerative agriculture requires land use demands such as urbanization, mining) may conflict with regenerative practices that promote ecosystem services and improving soil health through biological processes offer a unique opportunity while promoting biodiversity by adopting holistic approaches to mitigate climate change.

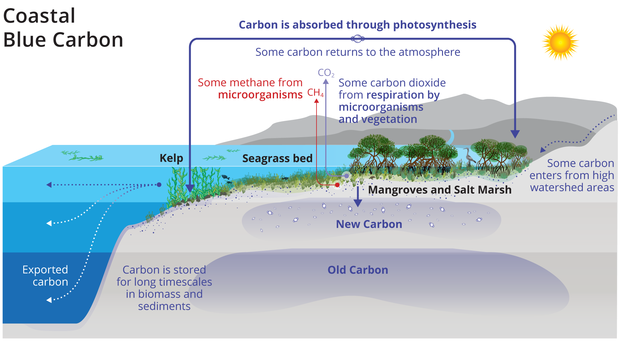
Blue-Carbon Projects are a type of carbon sequestration initiative that focuses on preserving, restoring, or enhancing marine ecosystems such as mangroves, salt marshes, kelp forests, coral reefs, and other coastal habitats. These projects aim to capture and store atmospheric CO2 in the form of organic matter within these underwater environments.
Key features of Blue-Carbon Projects:
- Marine ecosystem conservation: Protecting and restoring marine ecosystems that are rich in carbon-storing vegetation such as mangroves, salt marshes, or seagrasses.
- Carbon sequestration through photosynthesis: Marine plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, storing it within their biomass and sediments.
- Soil formation and sedimentation: As marine plants grow and die, they contribute to soil formation in coastal areas, which can store significant amounts of carbon for centuries or even millennia.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: By preserving these ecosystems, Blue-Carbon Projects help maintain the natural processes that regulate CO2 levels in the atmosphere.
Benefits of Blue-Carbon Projects:
- Climate change mitigation: These projects contribute to reducing atmospheric CO2 concentrations by sequestering carbon within marine ecosystems.
- Ecosystem services preservation: Protecting and restoring these coastal habitats maintains essential ecosystem functions such as shoreline stabilization, fisheries support, water filtration, and biodiversity conservation.
- Coastal resilience enhancement: Preserving or enhancing the health of these ecosystems can help protect communities from climate-related hazards like storm surges, erosion, and sea-level rise.
Examples of successful Blue-Carbon Projects:
- The Mangrove Forest Restoration Project in Indonesia, which has restored over 100 hectares (247 acres) of mangroves since its inception.
- The Kelp Forest Conservation Program in California, USA, aimed at protecting these underwater ecosystems and their associated carbon sequestration potential.
- The Coral Reef Trust's Blue Carbon Initiative in the Maldives, which promotes sustainable fishing practices while preserving coral reefs that store significant amounts of CO2.
Challenges and limitations:
- Monitoring and verification: Accurately measuring the carbon sequestered within these ecosystems can be complex due to factors like tidal cycles, water currents, or changes in vegetation density.
- Land-use conflicts: Coastal areas often face competing demands for land use (e.g., urbanization, agriculture), which may compromise ecosystem conservation efforts.
- Climate-related hazards: Rising sea levels and increased storm frequency can threaten the very existence of these ecosystems.
Despite these challenges, Blue-Carbon Projects offer a promising approach to climate change mitigation by leveraging the natural carbon sequestration potential of marine ecosystems.


Carbon Grassland Projects, also known as Carbon Farming or Regenerative Agriculture initiatives, focus on using agricultural practices to sequester and store atmospheric carbon dioxide in soils and vegetation of grasslands. These projects aim to promote sustainable land use, improve soil health, enhance biodiversity, and mitigate climate change.
Key features of Carbon Grassland Projects:
- Regenerative agriculture: Implementing farming techniques that prioritize soil conservation, organic amendments, cover cropping, reduced tillage, and integrated pest management.
- Soil carbon sequestration: Enhancing the capacity of soils to store carbon through practices like no-till or reduced-till farming, incorporating organic matter into the soil, and using cover crops.
- Grassland restoration: Restoring degraded grasslands by reintroducing native species, controlling invasive weeds, and promoting ecosystem services such as pollination and pest control.
- Livestock management: Implementing rotational grazing practices that promote healthy pastures, reduce erosion, and enhance soil fertility.
- Monitoring and verification: Tracking the project's carbon sequestration rates through regular monitoring of soil health indicators (e.g., soil organic matter content), vegetation growth metrics (e.g., above-ground biomass production), and greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits of Carbon Grassland Projects:
- Climate change mitigation: By storing atmospheric CO2 in soils, these projects contribute to reducing the global carbon footprint.
- Improved soil health: Regenerative agriculture practices enhance soil fertility, structure, and biodiversity, leading to increased crop yields and improved water retention capacity.
- Biodiversity conservation: Restoring grasslands promotes native species diversity, pollination services, and ecosystem resilience.
- Economic benefits: Carbon Grassland Projects can generate revenue through carbon credits sold on the market or by improving land values due to enhanced soil health.
Examples of successful Carbon Grassland Projects include:
- The Soil Health Institute's (SHI) Regenerative Agriculture Program in the United States, which promotes regenerative practices and provides technical assistance to farmers.
- The Australian Government's Emissions Reduction Fund (ERF), which supports carbon sequestration projects through various land use management techniques.
- The Kenyan-based organization, Green Belt Movement, which empowers local communities to restore degraded lands while promoting sustainable agriculture practices.
These initiatives demonstrate the potential for Carbon Grassland Projects to contribute positively to climate change mitigation and soil conservation efforts worldwide.
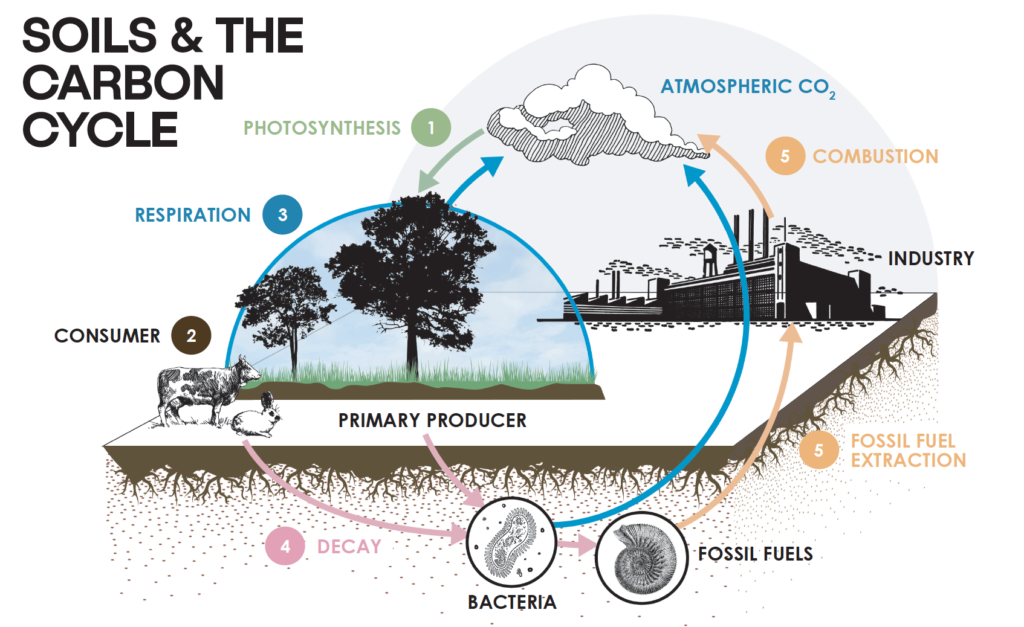
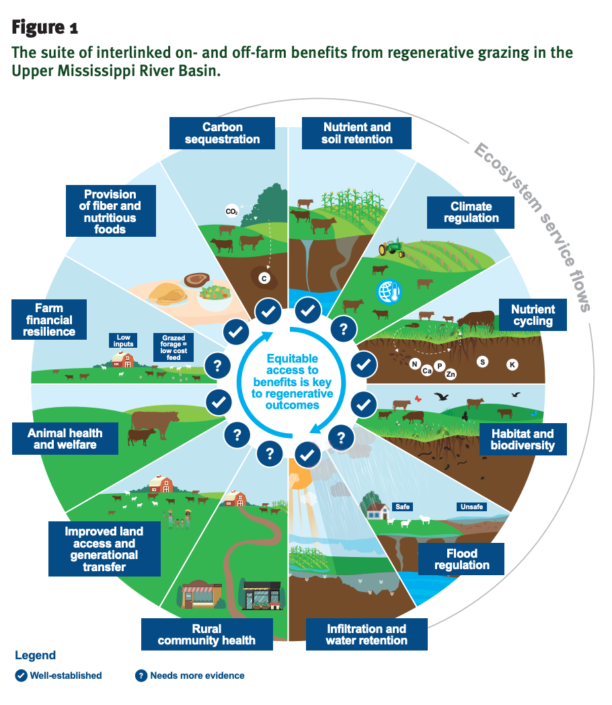
Regenerative Agriculture Carbon Sequestration refers to the process of using farming practices that promote soil health and biodiversity while capturing atmospheric CO2 in soils, plants, and other ecosystem components.
Key principles:
- Soil conservation: Implementing techniques like no-till or reduced-till farming, cover cropping, and incorporating organic amendments to minimize erosion and preserve soil structure.
- Carbon-rich crop rotations: Rotating crops that enhance carbon sequestration in soils through practices such as legume-based systems or using nitrogen-fixing plants.
- Organic matter addition: Adding compost, manure, or other organic materials to improve soil fertility while promoting microbial activity and enhancing carbon storage capacity.
- Cover cropping: Planting cover crops during off-seasons to protect the soil from erosion, add nutrients, and sequester CO2 through photosynthesis.
Carbon Sequestration Mechanisms:
- Soil Carbon Sequestration: Soil microorganisms break down organic matter into stable carbon compounds that can remain in soils for centuries.
- Plant Biomass Storage: Plants absorb atmospheric CO2 during growth and store it within their biomass, which is then returned to the soil as organic matter through decomposition or harvest.
- Soil Microbial Carbon Sequestration: Soil microorganisms contribute to carbon sequestration by breaking down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds that can be stored in soils.
Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture:
- Climate Change Mitigation: By capturing atmospheric CO2 and storing it within ecosystems, regenerative agriculture practices help mitigate climate change.
- Soil Health Improvement: These farming techniques enhance soil fertility, structure, and biodiversity while reducing erosion risk.
- Increased Crop Yields: Regenerative agriculture can lead to improved crop yields due to enhanced soil health and increased water retention capacity.
Examples of successful regenerative agriculture projects:
- The Soil Health Institute's (SHI) Regenerative Agriculture Program, which promotes regenerative practices through technical assistance, research, and education.
- The Rodale Institute's Farming Systems Trial, a long-term study on the effects of different farming systems on soil health, biodiversity, and carbon sequestration.
- The Savory Institute's Holistic Management approach, which integrates livestock grazing with regenerative agriculture practices to enhance ecosystem services.
Challenges and limitations:
- Scalability: Regenerative agriculture requires significant changes in land use management practices that can be challenging to scale up globally.
- Monitoring and verification: Accurately measuring carbon sequestration rates within these ecosystems is complex due to factors like soil type, climate conditions, or changes in vegetation density.
- Land-use conflicts: Competing demands for land use (e.g., urbanization, agriculture) can compromise ecosystem conservation efforts.
Despite these challenges, Regenerative Agriculture Carbon Sequestration offers a promising approach to mitigating climate change by leveraging the natural carbon sequestration potential of ecosystems while promoting soil health and biodiversity.



.jpg)
